A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Wound Care Products: Protecting and Promoting Healing
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Wound Care Products: Protecting and Promoting Healing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Wound Care Products: Protecting and Promoting Healing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Wound Care Products: Protecting and Promoting Healing

Wound care is an essential aspect of healthcare, encompassing the treatment of injuries, surgical incisions, and chronic conditions that affect skin integrity. Effective wound care products are crucial for promoting healing, preventing infection, and minimizing scarring. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse range of products available, providing a detailed understanding of their applications, benefits, and considerations for selection.
Understanding Wound Care Products: A Foundation for Effective Healing
Wound care products are designed to address specific needs based on the type, severity, and stage of healing. They facilitate a conducive environment for wound healing by:
- Protecting the wound from further injury: Products like bandages, dressings, and films act as a barrier, shielding the wound from external contaminants and trauma.
- Absorbing excess exudate: Dressings with absorbent properties manage wound drainage, promoting a clean and dry environment.
- Maintaining a moist wound environment: Moist wound healing is often optimal, and certain products contribute to this environment, facilitating cell migration and tissue regeneration.
- Delivering medication: Some products act as carriers for topical antibiotics, antiseptics, or growth factors, directly addressing specific wound challenges.
Categories of Wound Care Products: A Detailed Exploration
The landscape of wound care products is vast and diverse, offering tailored solutions for a wide range of needs. Here’s a breakdown of the key categories and their associated products:
1. Wound Cleansers:
- Purpose: Gentle removal of debris, bacteria, and foreign materials from the wound surface.
-
Types:
- Saline solution: A sterile, non-irritating solution, commonly used for initial wound cleansing.
- Antiseptic solutions: Contain ingredients like iodine or chlorhexidine to kill bacteria and reduce infection risk.
- Wound wash solutions: Specifically formulated for wound care, often containing gentle cleansing agents and moisturizers.
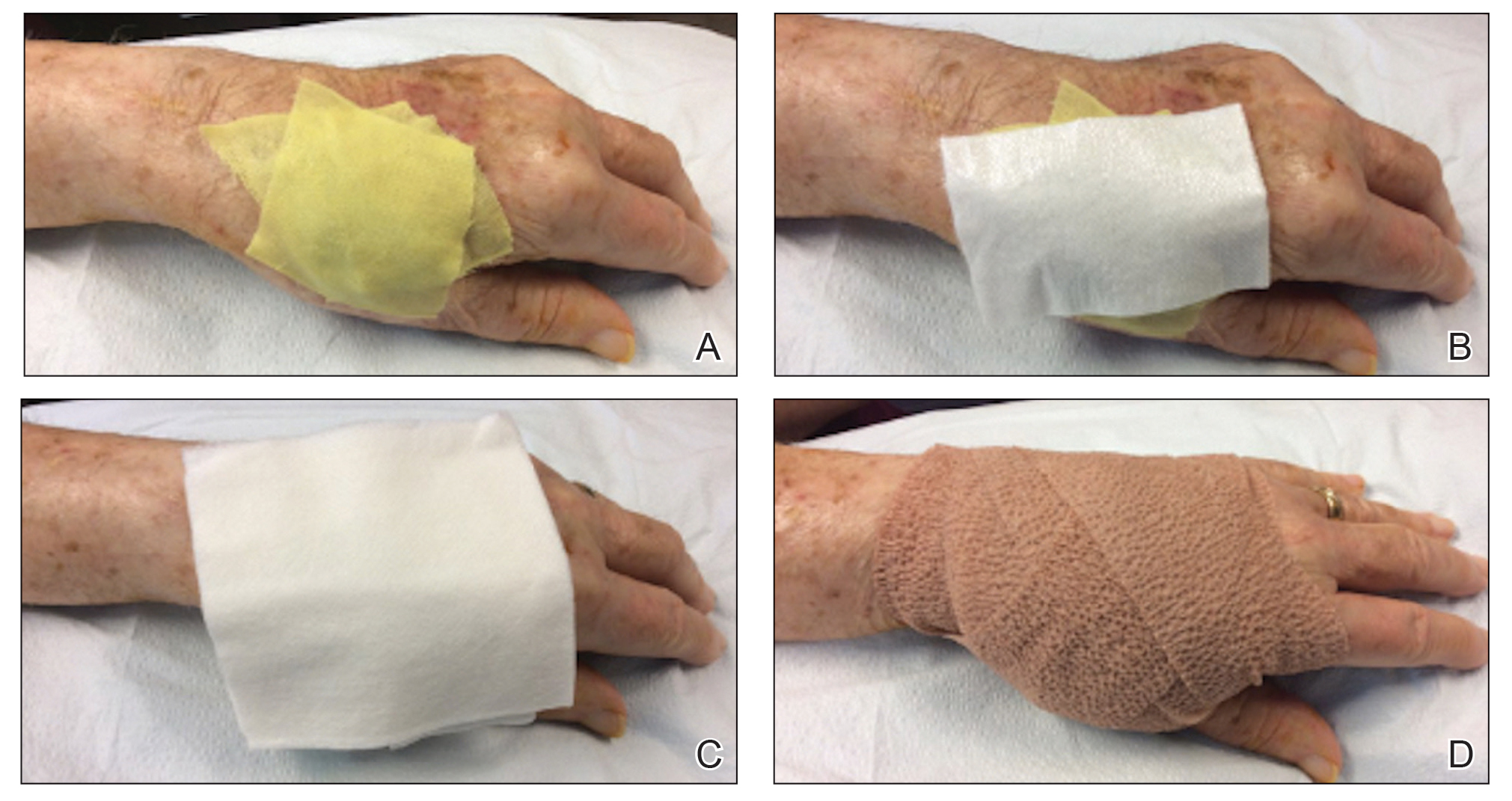
2. Dressings:
- Purpose: Cover and protect the wound, manage exudate, and provide a conducive healing environment.
-
Types:
- Gauze dressings: Versatile and inexpensive, available in various sizes and forms, including pads, rolls, and sponges.
- Hydrocolloid dressings: Form a gel-like barrier over the wound, promoting moisture retention and autolytic debridement (natural removal of dead tissue).
- Hydrofiber dressings: Highly absorbent, ideal for wounds with heavy exudate, providing a moist environment for healing.
- Foam dressings: Provide cushioning and absorption, suitable for wounds with moderate exudate.
- Film dressings: Transparent, semi-permeable, and breathable, allowing for visualization of the wound.
- Alginate dressings: Derived from seaweed, these dressings absorb exudate and form a gel, providing a moist environment.
- Silver dressings: Incorporate silver ions, which possess antimicrobial properties, reducing infection risk.
- Collagen dressings: Support wound healing by providing a scaffold for cell growth and tissue regeneration.
3. Topical Medications:
- Purpose: Address specific wound complications like infection, inflammation, or delayed healing.
-
Types:
- Antibiotics: Combat bacterial infections, available in various forms like creams, ointments, and solutions.
- Antiseptics: Reduce the risk of infection by killing bacteria on the wound surface.
- Growth factors: Promote cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, accelerating healing.
- Anti-inflammatory agents: Reduce pain and swelling associated with wound inflammation.
4. Wound Closure Devices:
- Purpose: Close wounds, minimizing scarring and promoting rapid healing.
-
Types:
- Sutures: Used for deep wounds, providing strong closure and minimizing infection risk.
- Staples: Similar to sutures, used for skin closure, particularly for large wounds.
- Steri-Strips: Adhesive strips used for superficial wounds, providing support and closure.
- Tissue adhesives: Liquid adhesives that bond skin edges together, minimizing scarring and facilitating rapid healing.
5. Wound Care Accessories:
- Purpose: Enhance wound care practices and optimize healing outcomes.
-
Types:
- Wound irrigation syringes: Used for flushing wounds with cleansing solutions, removing debris and bacteria.
- Wound measuring tools: Help track wound size and healing progress.
- Wound care tapes: Secure dressings and provide additional support.
- Compression bandages: Used for managing edema and promoting circulation, aiding in healing.
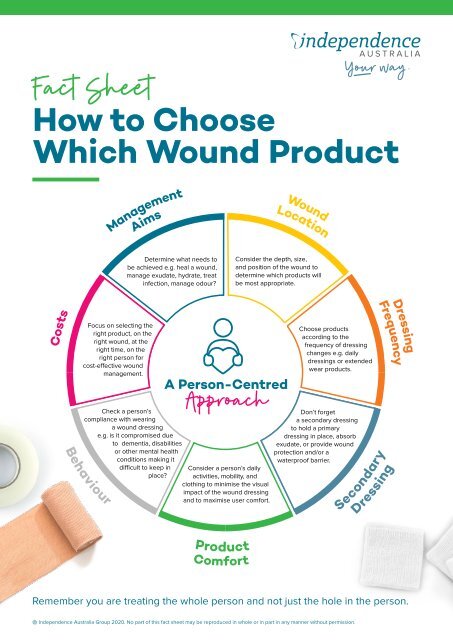
Choosing the Right Wound Care Products: A Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the appropriate wound care products is crucial for achieving optimal healing outcomes. Factors to consider include:
- Type and severity of the wound: Different products cater to specific wound types, such as pressure ulcers, burns, lacerations, and surgical incisions.
- Stage of healing: The healing process progresses through distinct stages, requiring different products to support each phase.
- Amount of exudate: Dressings need to be selected based on the volume of drainage to ensure proper management.
- Patient factors: Age, underlying health conditions, allergies, and medication use influence product selection.
- Cost and availability: Consider the affordability and accessibility of products, ensuring they are readily available.
Best Practices for Wound Care: Maximizing Healing Outcomes
- Thorough wound cleansing: Regularly clean the wound with appropriate solutions to remove debris and minimize infection risk.
- Proper dressing selection: Choose dressings that are appropriate for the wound type, stage of healing, and exudate level.
- Regular dressing changes: Change dressings as recommended by healthcare professionals to maintain a clean and optimal healing environment.
- Monitoring for signs of infection: Be vigilant for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and pus.
- Adhering to healthcare provider instructions: Follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals for wound care to ensure optimal outcomes.
FAQs on Wound Care Products: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What is the best way to clean a wound?
- Initial cleansing: Use a sterile saline solution to gently irrigate the wound, removing debris and bacteria.
- Subsequent cleansing: Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for cleaning the wound, using appropriate solutions and techniques.
2. How often should I change a wound dressing?
- Frequency: The frequency of dressing changes depends on the wound type, stage of healing, and amount of exudate. Consult with a healthcare provider for specific recommendations.
- Signs of needing a change: If the dressing becomes soaked, loose, or contaminated, it should be changed promptly.
3. What are the signs of a wound infection?
- Redness: The area around the wound may become red and inflamed.
- Swelling: The wound and surrounding area may become swollen.
- Warmth: The wound may feel warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Pain: Increased pain or tenderness around the wound.
- Pus: A yellow or green discharge may form around the wound.
4. Are there any natural remedies for wound healing?
- Honey: Possesses antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, promoting wound healing.
- Aloe vera: Soothes and moisturizes the wound, promoting tissue regeneration.
- Calendula: Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, aiding in wound healing.
- Essential oils: Some essential oils, like tea tree oil, have antimicrobial properties, but should be used with caution.
5. Can I use over-the-counter wound care products?
- Consult a healthcare provider: It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using any over-the-counter wound care products.
- Appropriate selection: Choose products that are specifically designed for wound care and appropriate for the type and severity of the wound.
Tips for Effective Wound Care: Maximizing Healing Potential
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly before and after caring for a wound.
- Keep the wound clean and dry: Regularly clean the wound and ensure it is dry between dressing changes.
- Avoid touching the wound: Limit contact with the wound to minimize contamination.
- Protect the wound from further injury: Avoid activities that could irritate or reopen the wound.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about a wound.
Conclusion: Empowering Healing through Informed Wound Care
Wound care is a crucial aspect of healthcare, ensuring optimal healing, minimizing complications, and promoting overall well-being. Understanding the diverse range of wound care products, their applications, and best practices for their use empowers individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to effective healing outcomes. This guide serves as a valuable resource, providing a comprehensive overview of the products available, their benefits, and key considerations for selection. By embracing informed wound care practices, individuals can promote healing and maintain their health and well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Wound Care Products: Protecting and Promoting Healing. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!