Navigating the Beauty Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cosmetic Product Business Plans
Related Articles: Navigating the Beauty Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cosmetic Product Business Plans
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Beauty Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cosmetic Product Business Plans. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Beauty Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cosmetic Product Business Plans

The global cosmetics market is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, characterized by fierce competition and a constant demand for innovation. Success in this arena requires a meticulous approach, starting with a well-structured and comprehensive business plan. This document serves as a roadmap, outlining the strategic direction, financial projections, and operational framework for a cosmetic product venture.
I. Defining the Business:
A. Executive Summary:
This concise overview provides a snapshot of the business, highlighting its key objectives, target market, and unique selling propositions. It should encapsulate the essence of the venture, attracting potential investors and stakeholders.
B. Company Description:
This section delves deeper into the company’s history, mission, and values. It should articulate the company’s core purpose and its long-term vision for growth and expansion within the cosmetics industry.
C. Products and Services:
A detailed description of the offered products is crucial. This section should encompass product features, benefits, target customer segments, and any unique formulations or technologies employed. It should also address the pricing strategy and any potential future product lines or expansions.
D. Market Analysis:
This section analyzes the current state of the cosmetic market, identifying industry trends, competitive landscape, and potential growth opportunities. It should consider:
- Target Market: Defining the specific consumer demographic the products cater to, including age, gender, income, lifestyle, and beauty preferences.
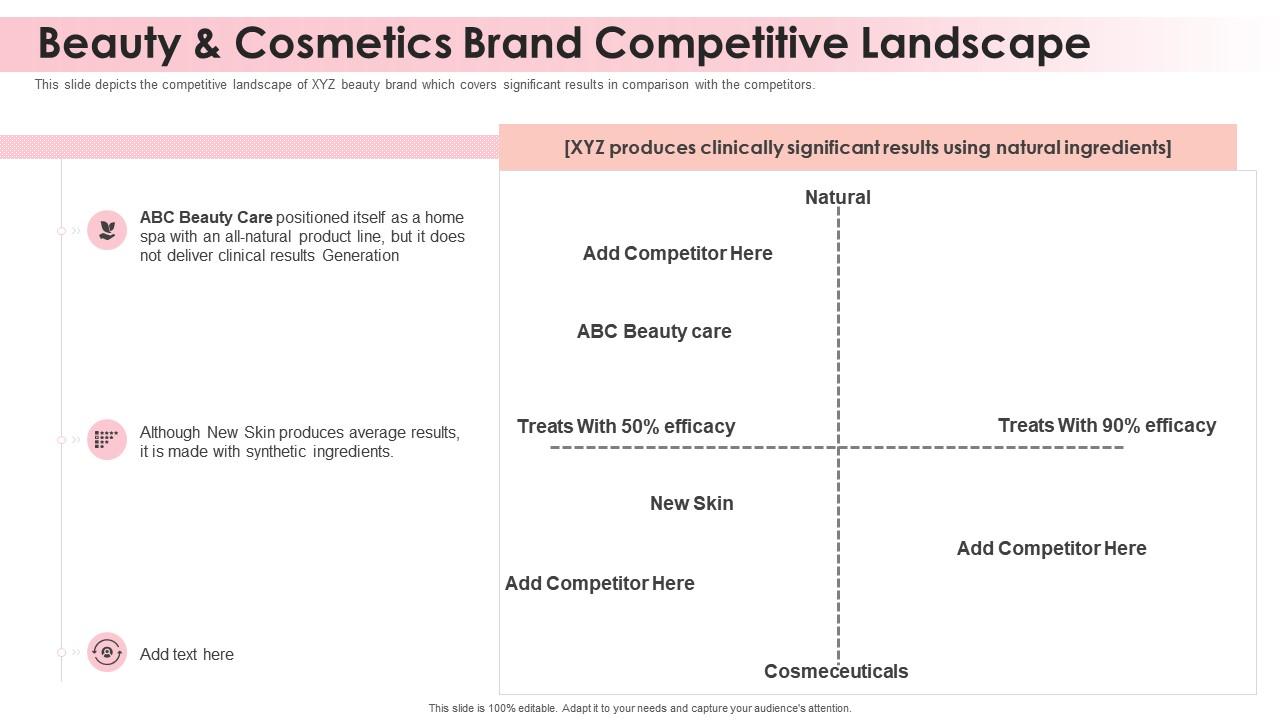
- Competitive Analysis: Identifying direct and indirect competitors, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, and evaluating potential market share.
- Market Trends: Analyzing emerging trends in the cosmetics industry, such as natural ingredients, sustainability, and personalized beauty solutions.
- Market Segmentation: Identifying distinct customer segments within the target market and tailoring product offerings and marketing strategies accordingly.
E. Marketing and Sales Strategy:
This section outlines the strategies for reaching the target market and achieving sales goals. It should include:
- Marketing Channels: Identifying appropriate channels for reaching the target audience, such as online platforms, social media, retail partnerships, and influencer marketing.
- Marketing Mix: Defining the specific marketing tools to be employed, including advertising, public relations, content marketing, and promotional activities.
- Sales Strategy: Establishing a clear approach for generating sales, including distribution channels, pricing strategies, and customer service protocols.
F. Management Team:
This section introduces the individuals responsible for leading the venture, highlighting their experience, skills, and expertise relevant to the cosmetics industry. It should demonstrate the team’s ability to navigate the complexities of the business and achieve its objectives.
II. Financial Projections:
A. Startup Costs:
This section outlines the initial investment required to launch the business, including costs associated with product development, manufacturing, packaging, marketing, and legal expenses.
B. Operating Expenses:
This section details the ongoing costs associated with running the business, including rent, utilities, salaries, inventory, and marketing expenses.
C. Revenue Projections:
This section forecasts future revenue based on anticipated sales volumes, pricing strategies, and market growth projections.
D. Profitability Analysis:
This section analyzes the projected profitability of the venture, considering both short-term and long-term perspectives. It should assess the business’s financial viability and its potential for generating returns on investment.
E. Funding Requirements:
This section outlines the specific financial resources required to launch and operate the business, including potential sources of funding such as loans, investments, and grants.
III. Operations and Implementation:
A. Production and Manufacturing:
This section details the production process, including sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing procedures, quality control measures, and packaging specifications. It should also address the scalability of production to meet anticipated demand.
B. Distribution and Logistics:
This section outlines the distribution strategy, including warehousing, shipping, and inventory management. It should ensure efficient delivery of products to customers and retailers.
C. Customer Service:
This section defines the customer service approach, emphasizing responsiveness, problem-solving, and building customer loyalty. It should address how customer feedback is collected and used to improve products and services.
D. Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
This section ensures compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, including product safety standards, labeling requirements, and environmental regulations. It should address any potential legal risks and mitigation strategies.
IV. Key Success Factors:
A. Innovation and Product Differentiation:
This section emphasizes the importance of developing unique and innovative products that stand out in a crowded market. It should highlight any proprietary technologies, formulations, or design elements that contribute to product differentiation.
B. Strong Brand Identity:
This section emphasizes the importance of establishing a clear and compelling brand identity that resonates with the target market. It should address brand positioning, messaging, and visual elements that contribute to brand recognition and customer loyalty.
C. Effective Marketing and Sales:
This section highlights the importance of reaching the target market through appropriate channels and utilizing effective marketing strategies to generate sales. It should address the importance of data-driven marketing and customer segmentation.
D. Strong Customer Relationships:
This section emphasizes the importance of building strong customer relationships through exceptional customer service, loyalty programs, and personalized experiences. It should address the value of collecting and analyzing customer feedback to improve products and services.
E. Financial Management:
This section highlights the importance of sound financial management, including accurate budgeting, cost control, and efficient resource allocation. It should address the importance of monitoring key financial metrics and making informed financial decisions.
V. Risks and Mitigation Strategies:
A. Market Risks:
This section identifies potential market risks, such as changes in consumer preferences, economic downturns, and competitive pressures. It should outline mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these risks, such as product diversification, market research, and competitive analysis.
B. Operational Risks:
This section identifies potential operational risks, such as production delays, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues. It should outline mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these risks, such as contingency planning, risk management protocols, and supplier diversification.
C. Financial Risks:
This section identifies potential financial risks, such as funding shortages, cash flow problems, and unfavorable economic conditions. It should outline mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these risks, such as financial forecasting, budgeting, and securing alternative sources of funding.
D. Legal and Regulatory Risks:
This section identifies potential legal and regulatory risks, such as changes in regulations, product liability claims, and intellectual property infringement. It should outline mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these risks, such as legal counsel, compliance procedures, and insurance coverage.
VI. Conclusion:
The business plan serves as a comprehensive roadmap for navigating the competitive landscape of the cosmetics industry. By thoroughly addressing each aspect of the venture, from product development to marketing and operations, the plan provides a solid foundation for success. It should be viewed as a dynamic document, subject to ongoing review and revision as the business evolves and adapts to changing market conditions.
FAQs by Business Plan for Cosmetic Products:
Q: What are the most important elements of a cosmetic product business plan?
A: The most crucial elements include a thorough market analysis, a detailed product description, a well-defined marketing and sales strategy, and comprehensive financial projections. These components provide a clear understanding of the target market, the competitive landscape, and the financial viability of the venture.
Q: How can a business plan help secure funding for a cosmetic product venture?
A: A well-structured business plan demonstrates the viability and potential of the venture, attracting investors and lenders. It provides a clear roadmap for success, outlining the strategic direction, financial projections, and operational framework.
Q: How frequently should a business plan be reviewed and updated?
A: A business plan should be reviewed and updated at least annually, or more frequently if there are significant changes in the market, the company’s operations, or its financial performance. This ensures the plan remains relevant and serves as an effective guide for decision-making.
Q: What are some common pitfalls to avoid when developing a business plan for a cosmetic product venture?
A: Common pitfalls include unrealistic financial projections, inadequate market research, and a lack of focus on product differentiation. It is crucial to conduct thorough research, develop a realistic plan, and emphasize the unique value proposition of the products.
Tips by Business Plan for Cosmetic Products:
- Focus on a niche market: Target a specific customer segment with tailored products and marketing messages.
- Emphasize product innovation: Develop unique formulations, ingredients, or packaging that differentiate the products from competitors.
- Build a strong brand identity: Create a memorable brand name, logo, and messaging that resonates with the target market.
- Leverage digital marketing: Utilize social media, online advertising, and content marketing to reach the target audience effectively.
- Develop strong customer relationships: Provide exceptional customer service, collect feedback, and personalize the customer experience.
Conclusion:
A well-crafted business plan is essential for success in the dynamic and competitive world of cosmetics. By carefully defining the business, conducting thorough market research, developing a comprehensive marketing and sales strategy, and addressing potential risks, entrepreneurs can position their ventures for growth and profitability. The business plan serves as a roadmap, guiding the company’s strategic direction, financial decisions, and operational execution, ultimately contributing to the long-term success of the venture.

![Cosmetic Business Plan Template & How-To Guide [Updated 2024]](https://www.growthink.com/wp-content/uploads/cosmetic-business-plan.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Beauty Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Cosmetic Product Business Plans. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
