Navigating the Landscape of Eczema Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Strategies
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Eczema Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Strategies
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Eczema Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Strategies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Eczema Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Strategies
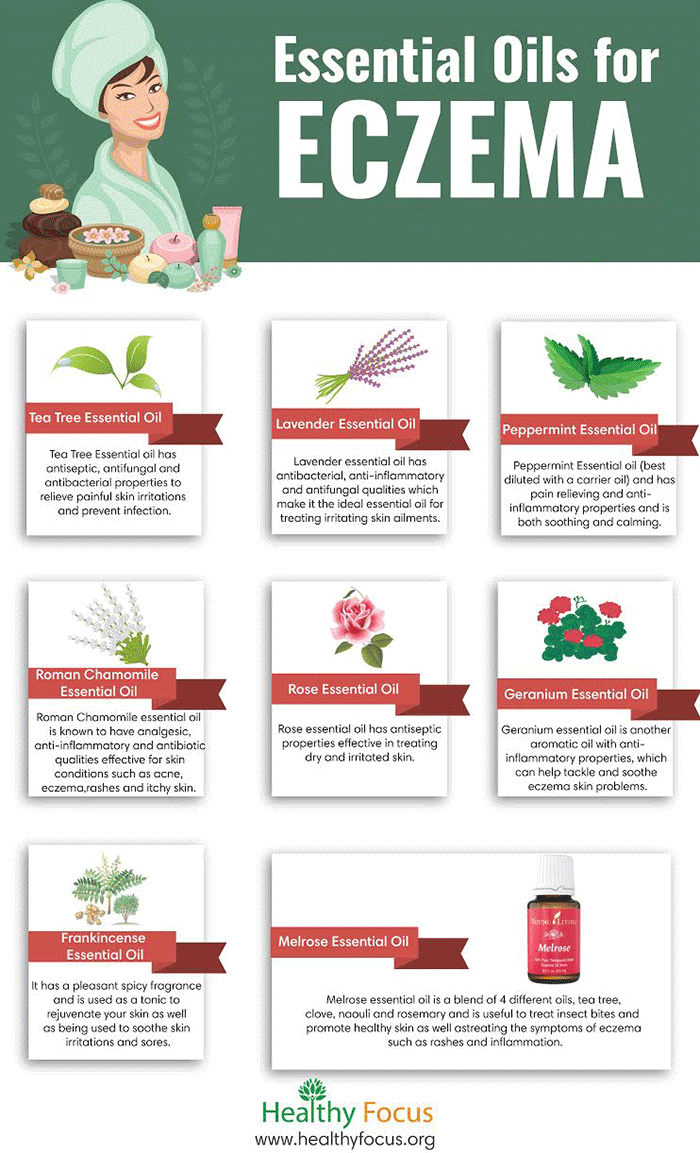
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and often dry patches. While there is no cure for eczema, a variety of treatments and products can effectively manage its symptoms and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide delves into the best products available for eczema, addressing the complexities of this condition with a focus on evidence-based approaches and practical advice.
Understanding the Spectrum of Eczema Products:
Eczema management involves a multi-pronged approach, encompassing topical treatments, oral medications, and lifestyle modifications. Products for eczema fall into several categories, each addressing specific aspects of the condition:
1. Topical Treatments:
-
Emollients and Moisturizers: These are the cornerstone of eczema treatment. They work by replenishing the skin’s natural barrier, preventing moisture loss, and reducing dryness.
- Ceramides: These lipids are naturally found in the skin and play a crucial role in maintaining its barrier function. Ceramides are often incorporated into moisturizers for eczema, restoring the skin’s protective layer.
- Hyaluronic Acid: This humectant attracts and retains moisture, keeping the skin hydrated and supple.
- Oils: Oils like coconut oil, olive oil, and jojoba oil can provide a protective barrier and soothe irritated skin. However, it is essential to choose oils specifically formulated for eczema, as some can be comedogenic (pore-clogging).
- Corticosteroids: These are potent anti-inflammatory medications available in various strengths and formulations, from creams and ointments to lotions and sprays. They are highly effective in reducing inflammation, itching, and redness associated with eczema. However, prolonged use can lead to skin thinning and other side effects, necessitating careful monitoring and adherence to prescribed usage guidelines.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: These topical medications, like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, suppress the immune system, reducing inflammation and itching. They are often used for maintenance therapy or in cases where corticosteroids are not suitable.
- Antihistamines: These medications, available in both topical and oral forms, block the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction. They can help reduce itching and inflammation, but their effectiveness in eczema is limited.
- Antiseptics: These agents, such as benzoyl peroxide and chlorhexidine, help control bacterial infections that can exacerbate eczema. They are particularly useful in cases of infected eczema.
2. Oral Medications:
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines, like cetirizine and fexofenadine, can help reduce itching and improve sleep quality. However, their effectiveness in eczema is limited.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications, such as cyclosporine and azathioprine, suppress the immune system, reducing inflammation and itching. They are typically used for severe, widespread eczema that does not respond to other treatments.
- Biologics: These are newer medications that target specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process. They are effective in treating severe eczema, but they are expensive and require close monitoring.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Identifying and Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers like allergens, irritants, and stress can significantly improve eczema management. Common triggers include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, certain foods, harsh soaps, and detergents.
- Regular Moisturizing: Maintaining a consistent moisturizing routine is crucial for preventing dry skin and reducing eczema flare-ups. Apply emollients liberally and frequently, especially after bathing.
- Warm Baths: Warm, short baths can help soothe irritated skin. Avoid hot water and harsh soaps, opting for gentle, fragrance-free cleansers instead.
- Proper Clothing: Choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from soft, natural fabrics like cotton. Avoid wool and synthetic fibers, which can irritate sensitive skin.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help alleviate symptoms.
Navigating the Product Landscape: Choosing the Right Products for Eczema:
With a plethora of products available, choosing the right ones for individual needs can seem daunting. Consider the following factors:
- Severity of Eczema: The severity of eczema dictates the type and strength of treatment required. Mild eczema may respond to emollients and over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams. Moderate to severe eczema may necessitate prescription-strength topical corticosteroids or other medications.
- Age and Skin Sensitivity: Different products are suitable for different ages and skin sensitivities. For infants and young children, choose gentle, fragrance-free products specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
- Individual Triggers: Knowing your specific triggers is essential for choosing products that minimize irritation and flare-ups.
- Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: Consulting a dermatologist or other healthcare professional is crucial for determining the best course of treatment and selecting appropriate products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Eczema Products:
1. What are the best emollients for eczema?
Numerous emollients are effective for eczema. Some popular choices include:
- CeraVe Moisturizing Cream: This cream contains ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and other skin-soothing ingredients, making it a good option for dry, sensitive skin.
- Eucerin Original Healing Cream: This cream is formulated with ceramides and other moisturizing agents to restore the skin’s natural barrier.
- Aveeno Skin Relief Moisturizing Lotion: This lotion contains colloidal oatmeal, which has anti-inflammatory properties and soothes itchy skin.
2. Are there any natural remedies for eczema?
While some natural remedies may provide temporary relief, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using them, especially for infants and children. Some commonly cited natural remedies include:
- Colloidal Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties and can soothe itchy skin.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil can provide a protective barrier and soothe irritated skin. However, it can be comedogenic, so use it with caution.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties and can be applied topically to soothe irritated skin.
3. How often should I apply emollients?
Apply emollients liberally and frequently, especially after bathing. For optimal results, apply them at least twice daily.
4. What are the side effects of corticosteroids?
Prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to skin thinning, stretch marks, and other side effects. It is important to use them as directed by a healthcare professional and to monitor for any adverse reactions.
5. Are there any safe alternatives to corticosteroids?
Calcineurin inhibitors, like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are safe alternatives to corticosteroids for some individuals. However, they are not suitable for everyone and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Tips for Effective Eczema Management:
- Maintain a Consistent Routine: Regular moisturizing, bathing, and medication application are essential for managing eczema.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Keeping a journal to track potential triggers can help identify and avoid them.
- Dress Comfortably: Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from soft, natural fabrics.
- Use Gentle Cleansers: Avoid harsh soaps and detergents, choosing gentle, fragrance-free alternatives instead.
- Protect Skin from Sun: Apply sunscreen regularly, even on cloudy days, as sun exposure can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Conclusion:
Eczema management is a journey, not a destination. Finding the right products and strategies for individual needs requires patience, persistence, and collaboration with a healthcare professional. By understanding the spectrum of eczema products, their mechanisms of action, and their potential benefits and risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plan and work towards achieving better skin health and quality of life.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Eczema Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Strategies. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!