The Fatigue Factor: Understanding How Medications Can Impact Energy Levels
Related Articles: The Fatigue Factor: Understanding How Medications Can Impact Energy Levels
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Fatigue Factor: Understanding How Medications Can Impact Energy Levels. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Fatigue Factor: Understanding How Medications Can Impact Energy Levels

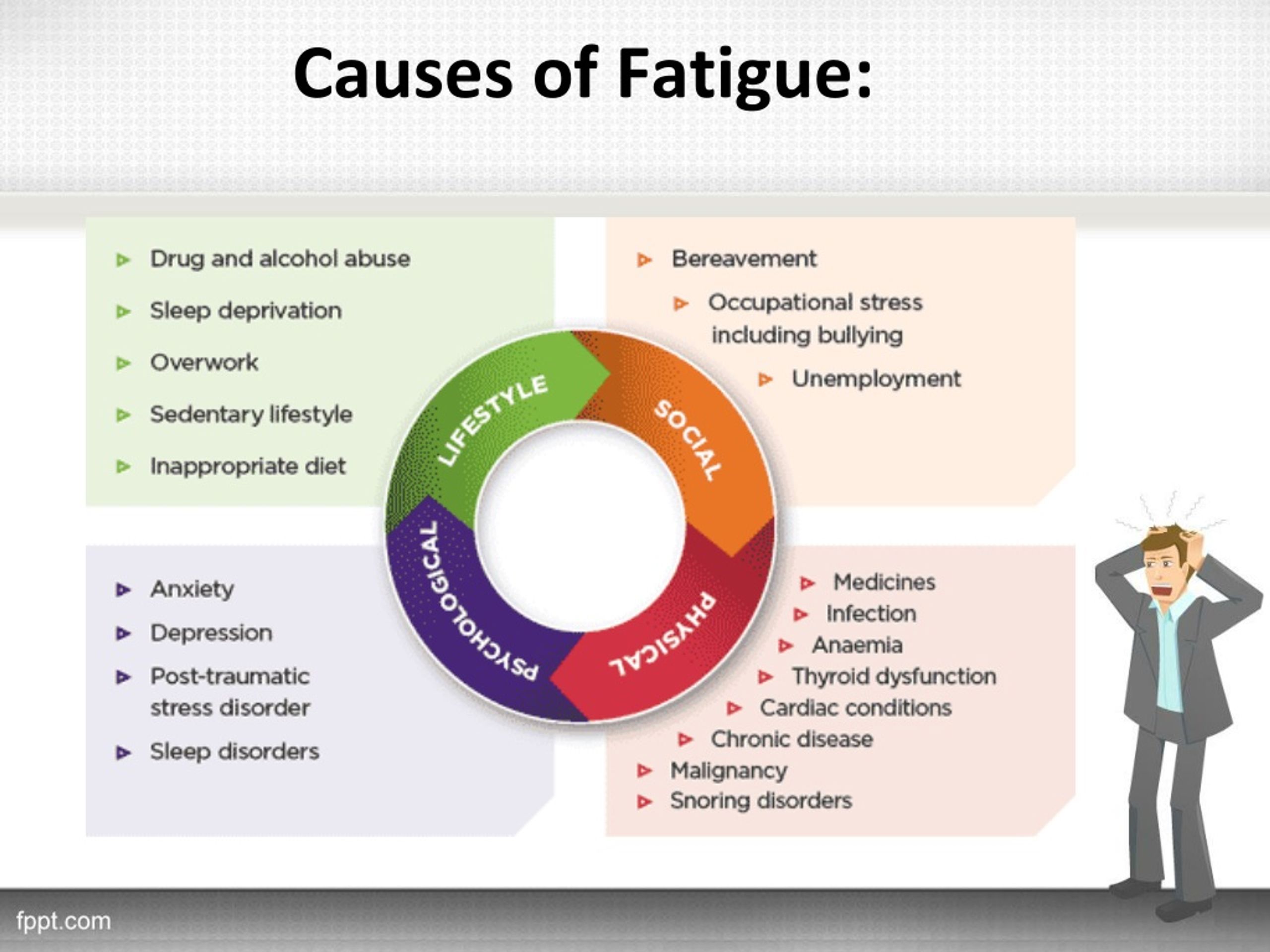
Fatigue, a common complaint across various demographics, can have numerous underlying causes. While lifestyle factors like stress, lack of sleep, and poor diet play a significant role, medications are often overlooked as a potential contributor. Understanding how different medications can influence energy levels is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals.
The Complexities of Medication-Induced Fatigue:
The relationship between medications and fatigue is complex and multifaceted. It is not simply a matter of one medication causing fatigue in all individuals. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
- Pharmacological Mechanisms: Certain medications exert their therapeutic effects by influencing the body’s neurotransmitters, specifically those involved in regulating wakefulness and sleep. For example, antidepressants, antihistamines, and certain anti-anxiety medications can affect the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, potentially leading to drowsiness or fatigue.
-
Side Effects: Many medications, even those not directly targeting the central nervous system, can have fatigue as a known side effect. This can be due to various reasons, including:
- Metabolic Changes: Some medications can disrupt the body’s metabolic processes, affecting energy production and utilization.
- Muscle Weakness: Certain medications can cause muscle weakness or pain, leading to reduced physical activity and increased fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some medications can cause nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, leading to dehydration and fatigue.
- Drug Interactions: The combination of multiple medications can increase the likelihood of fatigue. When medications interact, their effects can be amplified or altered, leading to unexpected side effects, including fatigue.
- Individual Variability: The same medication can have different effects on different individuals. Factors like age, genetics, health status, and even the time of day medication is taken can influence the experience of fatigue.
Common Medications Associated with Fatigue:
While fatigue can be a side effect of numerous medications, some classes are more commonly associated with this symptom. These include:
- Antihistamines: Used for allergies and colds, antihistamines can block histamine, a neurotransmitter involved in wakefulness. This can lead to drowsiness, especially with first-generation antihistamines.
- Antidepressants: Many antidepressants, particularly those targeting serotonin and norepinephrine, can cause fatigue, especially in the initial stages of treatment. This usually subsides as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Antipsychotics: Used for treating mental health conditions, antipsychotics can affect dopamine and serotonin levels, leading to fatigue and sedation.
- Anti-anxiety Medications: Benzodiazepines and other anti-anxiety medications can cause drowsiness and fatigue, particularly when taken in higher doses or combined with alcohol.
- Muscle Relaxants: These medications can cause fatigue by affecting muscle function and reducing physical activity.
- Opioids: Used for pain management, opioids can cause drowsiness and fatigue, especially at higher doses.
- Chemotherapy Drugs: Many chemotherapy drugs can cause fatigue as a side effect due to their impact on cells and the body’s overall energy production.
Addressing Medication-Induced Fatigue:
If you suspect medication is contributing to your fatigue, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They can assess your situation, review your medication list, and determine the best course of action. This may involve:
- Adjusting Medication Dosage: In some cases, reducing the dosage of a medication can alleviate fatigue without compromising its effectiveness.
- Switching Medications: If fatigue is a persistent and bothersome side effect, your doctor might recommend switching to a different medication with a lower risk of fatigue.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and getting adequate sleep can often help mitigate fatigue, even when caused by medication.
- Supplements: In some cases, supplements like vitamin D, iron, or magnesium may be helpful in combating fatigue. However, it is crucial to discuss any potential supplements with your doctor before taking them.
FAQs about Medication-Induced Fatigue:
1. How long does medication-induced fatigue typically last?
The duration of fatigue varies depending on the medication and individual factors. For some medications, fatigue may be a temporary side effect that subsides within a few days or weeks. However, for others, it can persist for longer periods, even months or years.
2. Can I stop taking my medication if I’m experiencing fatigue?
Never stop taking your medication without consulting your healthcare provider. Abruptly discontinuing medication can have serious consequences. Your doctor can adjust your medication or recommend alternative options if fatigue is a significant concern.
3. What are some natural remedies for medication-induced fatigue?
While natural remedies can be helpful for general fatigue, they may not always address medication-induced fatigue. It is essential to consult with your doctor before trying any natural remedies, as they can interact with your medications.
4. Is medication-induced fatigue a sign of something more serious?
While fatigue can be a common side effect of medication, it can also be a symptom of other underlying health conditions. If you experience persistent fatigue, it is important to see your doctor to rule out any other potential causes.
Tips for Managing Medication-Induced Fatigue:
- Communicate with Your Doctor: Openly discuss any fatigue you experience with your doctor, providing details about the timing and severity of the symptom.
- Keep a Medication Log: Track your medications, including dosages and times taken. This information can be helpful in identifying potential patterns or triggers for fatigue.
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help restore energy levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can worsen fatigue. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Choose nutrient-rich foods that provide sustained energy.
- Exercise Regularly: Moderate exercise can improve energy levels and overall well-being.
- Reduce Stress: Stress can exacerbate fatigue. Explore stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion:
Medication-induced fatigue is a common concern that can significantly impact quality of life. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, recognizing potential triggers, and actively communicating with healthcare providers, individuals can work towards managing this side effect and minimizing its impact. Remember, fatigue should not be ignored. It is essential to seek medical advice and explore appropriate strategies to alleviate this symptom and maintain overall well-being.

.jpg.aspx?width=600u0026height=600)


.jpg.aspx?width=600u0026height=600)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Fatigue Factor: Understanding How Medications Can Impact Energy Levels. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!