Understanding the Complexities of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Complexities of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complexities of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complexities of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Skin cancer, a disease characterized by abnormal cell growth in the skin, is a significant public health concern. It is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with millions of cases diagnosed annually. While the majority of skin cancers are treatable, early detection and prevention are crucial to minimizing the risk of complications and maximizing survival rates. This article delves into the intricate factors that contribute to the development of skin cancer, emphasizing the importance of understanding and mitigating these risks.
The Sun: A Major Culprit
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a primary driver of skin cancer. The sun emits two main types of UV radiation: UVA and UVB. Both can damage DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can eventually cause uncontrolled cell growth, the hallmark of cancer.
- UVA: This type of radiation penetrates deeper into the skin and contributes to premature aging, wrinkles, and skin thickening. It is also associated with the development of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
- UVB: Primarily responsible for sunburn, UVB radiation directly damages DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers.
Beyond the Sun: Other Contributing Factors
While sun exposure is the most significant risk factor, other factors can also contribute to skin cancer development.
- Tanning Beds and Lamps: These devices emit high levels of UVA radiation, posing a similar risk to sun exposure. Studies have shown that frequent use of tanning beds increases the risk of melanoma by 75%.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of skin cancer are at a higher risk. This suggests a genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, freckles, and light hair are more susceptible to skin cancer due to lower levels of melanin, the pigment that protects skin from UV radiation.
- Age: Skin cancer is more common in older adults as cumulative sun exposure over a lifetime increases the risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressant medications, are more vulnerable to skin cancer.
- Certain Genetic Syndromes: Individuals with certain genetic syndromes, such as Xeroderma pigmentosum, are highly susceptible to skin cancer due to deficiencies in DNA repair mechanisms.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic and some pesticides, has been linked to an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Previous Skin Cancer: Having had skin cancer before increases the risk of developing another skin cancer.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment and improved outcomes. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are essential.
- Self-Examinations: It is recommended to check your skin monthly for any changes, including new moles, sores that don’t heal, or changes in existing moles.
- Professional Skin Checks: Regular checkups by a dermatologist are essential, particularly for individuals with a family history of skin cancer or those with risk factors like fair skin.
Prevention Strategies: Shielding Yourself from Harm
While it is impossible to completely eliminate sun exposure, several preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
-
Sun Protection:
- Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every two hours, even on cloudy days.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat when outdoors.
- Seek Shade: Avoid prolonged sun exposure during peak hours (10 AM to 4 PM).
- Tanning Bed Avoidance: Refrain from using tanning beds or sunlamps.
- Regular Skin Exams: Conduct monthly self-examinations and schedule regular professional skin checks.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and avoid smoking.
Understanding the Different Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is broadly categorized into two main types: melanoma and non-melanoma.
- Melanoma: This is the deadliest form of skin cancer, accounting for a small percentage of cases but causing the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma originates in melanocytes, cells that produce melanin. It can develop anywhere on the body and often appears as a mole that changes in size, shape, or color.
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: This category includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These are less aggressive than melanoma and are typically treated successfully. Basal cell carcinoma originates in the basal layer of the epidermis, the outer layer of skin, and often appears as a pearly or waxy bump. Squamous cell carcinoma arises in the squamous cells of the epidermis and can present as a firm, red nodule or a flat, scaly patch.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it safe to tan?
A: No, tanning is not safe. Tanning beds and sun exposure both emit harmful UV radiation that can damage skin cells and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Q: Can I get skin cancer from a single sunburn?
A: While a single sunburn may not immediately cause skin cancer, it can contribute to cumulative sun damage over time, increasing the risk of developing the disease later in life.
Q: How often should I use sunscreen?
A: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every two hours, even on cloudy days.
Q: What are the early signs of skin cancer?
A: Look for any changes in moles, including new moles, sores that don’t heal, or changes in existing moles. Other signs include bumps, growths, or sores that are unusual or different from other skin lesions.
Q: What are the treatment options for skin cancer?
A: Treatment options vary depending on the type and stage of skin cancer. Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Tips for Protecting Your Skin
- Check the UV Index: The UV Index is a measure of the strength of the sun’s UV radiation. Avoid prolonged sun exposure when the UV Index is high.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from harmful UV radiation by wearing sunglasses that block 99-100% of UVA and UVB rays.
- Avoid Sunbathing: Sunbathing is a significant risk factor for skin cancer. Instead, opt for indoor activities or seek shade when outdoors.
- Educate Children: Teach children about sun safety from a young age to instill healthy habits.
- Consult a Dermatologist: Schedule regular skin checks with a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or other risk factors.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a preventable and treatable disease. By understanding the risk factors, practicing sun safety measures, and undergoing regular skin checks, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease. Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes, highlighting the importance of proactive measures to protect skin health.




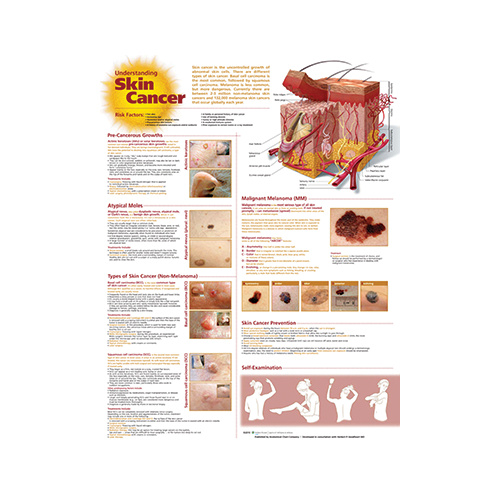



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complexities of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!