Unraveling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Guide to 3D Models and Their Applications
Related Articles: Unraveling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Guide to 3D Models and Their Applications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Guide to 3D Models and Their Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Guide to 3D Models and Their Applications

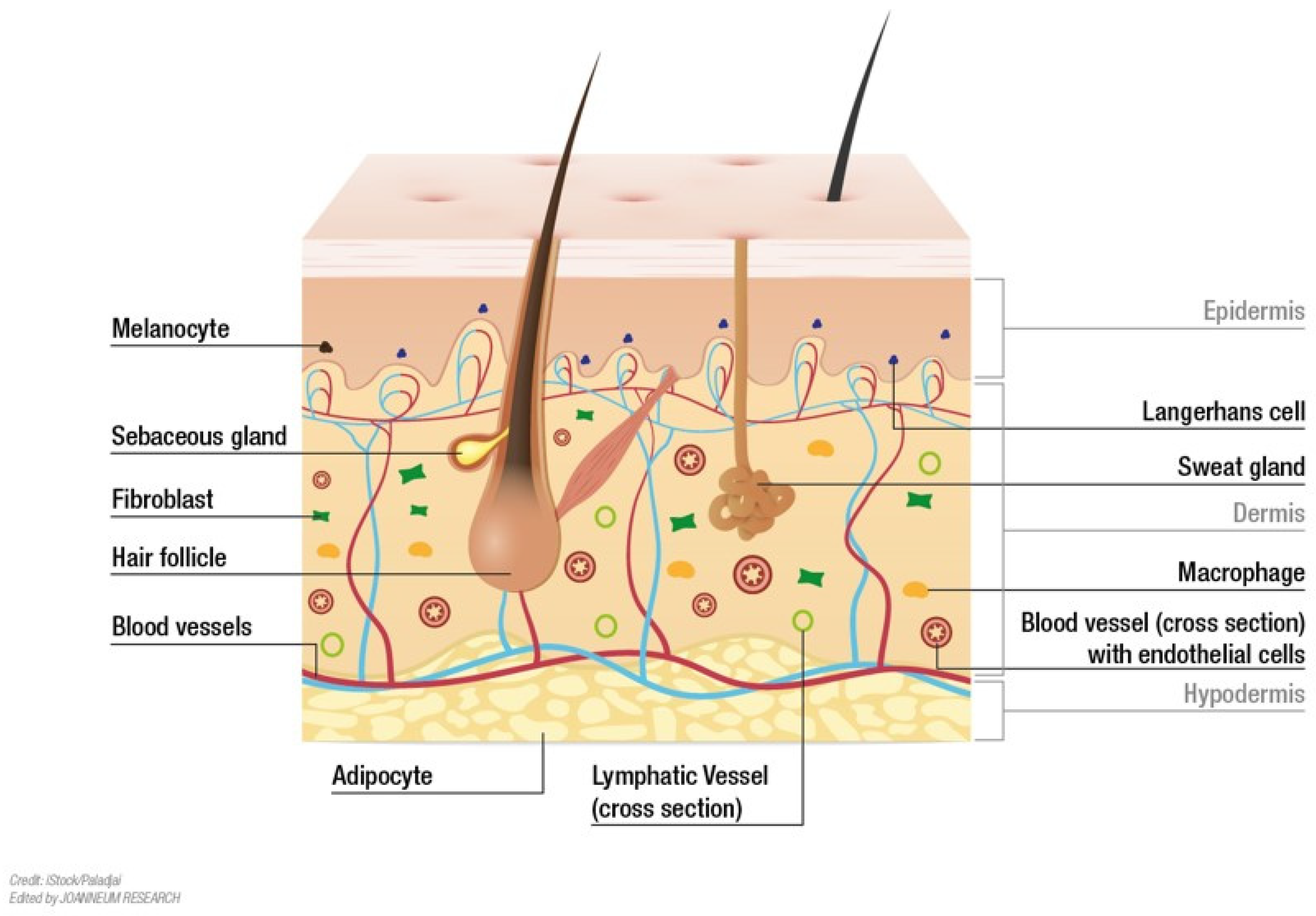
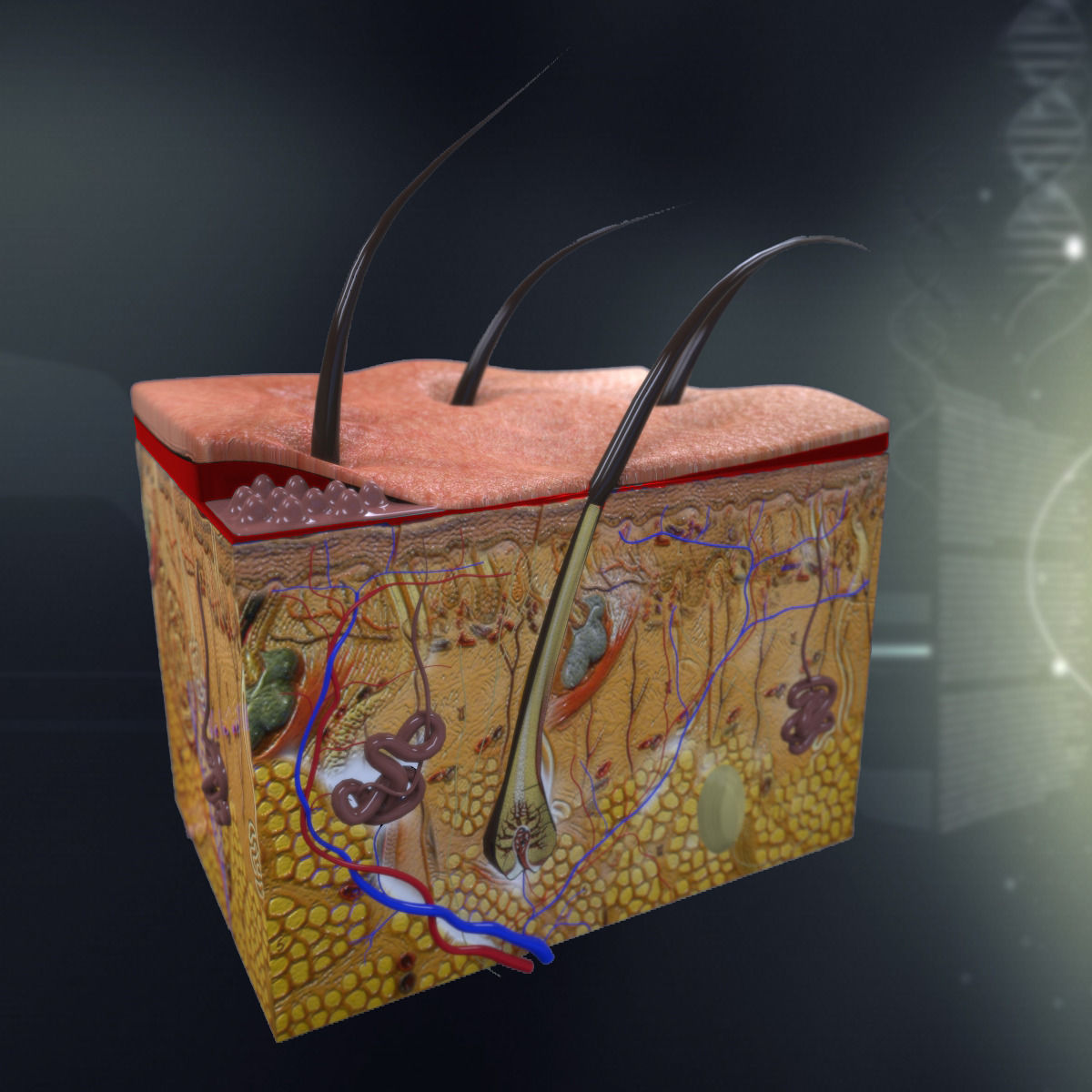
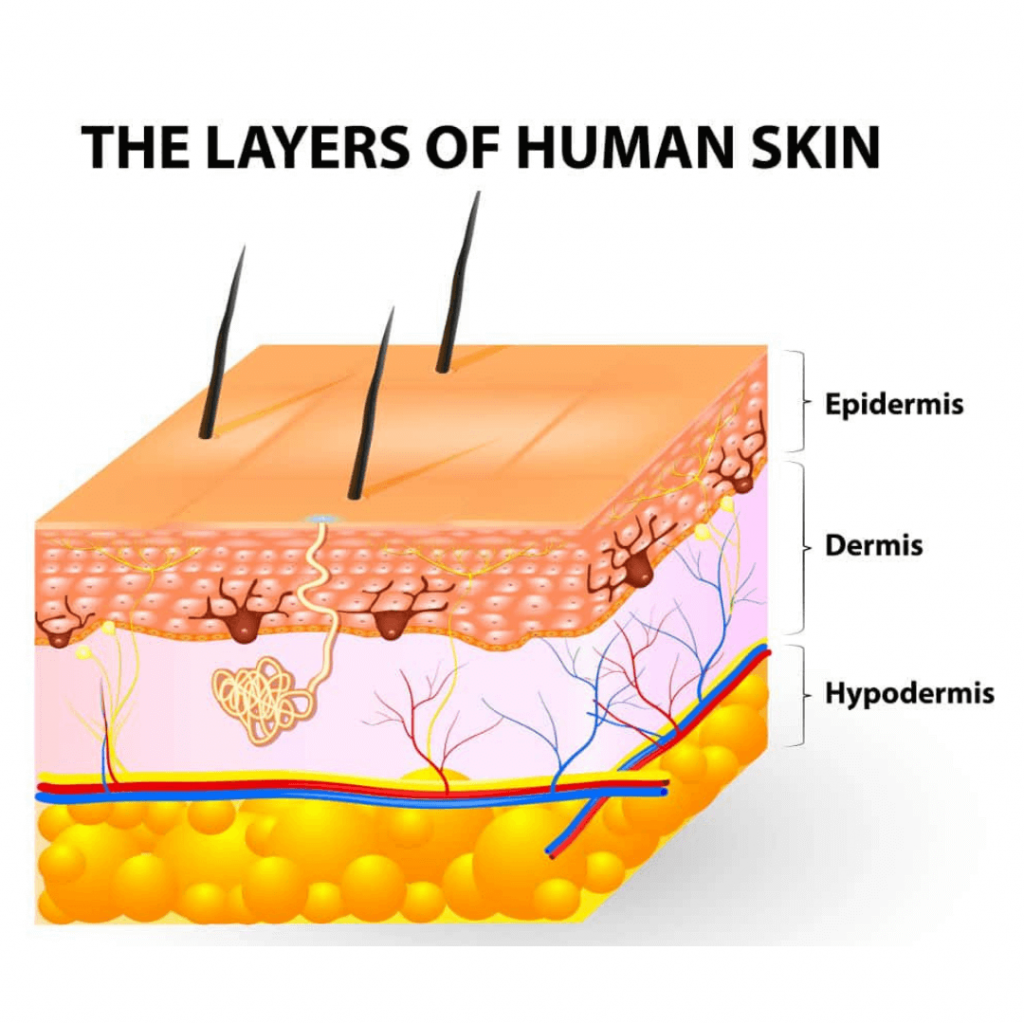
The human skin, our largest organ, is a marvel of biological engineering. It serves as a protective barrier against the environment, regulates temperature, and plays a crucial role in sensation and immunity. Understanding its intricate structure and functions is essential for medical professionals, researchers, and educators alike.
In recent years, the advent of 3D modeling technology has revolutionized the way we visualize and interact with complex biological systems. This technology offers a unique opportunity to explore the intricacies of human skin in an interactive and immersive manner.
The Power of 3D Skin Models
3D models of human skin provide a powerful tool for:
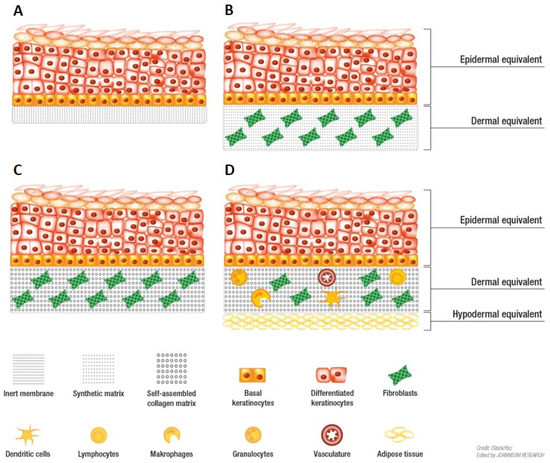
- Visualization and Understanding: They enable a deeper understanding of the skin’s layered structure, from the outermost epidermis to the innermost dermis and subcutaneous fat. Users can rotate, zoom, and dissect the model to explore individual components and their relationships.
- Educational Applications: 3D models are invaluable for students of biology, dermatology, and other related fields. They provide a visual and interactive learning experience, facilitating comprehension and retention of complex anatomical and physiological concepts.
- Research and Development: Researchers utilize 3D models to simulate various skin conditions, test the efficacy of treatments, and explore the impact of environmental factors on skin health. This allows for cost-effective and ethical experimentation, replacing traditional animal models in some cases.
- Patient Education and Communication: 3D models can be used to explain skin conditions to patients in a clear and engaging manner, enhancing their understanding of their diagnosis and treatment options. This improved communication fosters patient empowerment and adherence to treatment plans.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Applications: Integrating 3D skin models with VR and AR technologies allows for immersive and interactive experiences. This can be particularly beneficial for training medical professionals, conducting patient education, and developing new diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Finding Free 3D Skin Models
While commercial software and databases offer high-quality 3D models, several resources provide free access to a variety of skin models for educational and research purposes. These resources typically offer models with varying levels of detail and complexity, catering to diverse needs and interests.
Tips for Selecting and Using 3D Skin Models
- Define Your Needs: Consider the specific purpose for which you require the model. For educational purposes, a basic model with clear labeling might suffice, while research may necessitate a highly detailed model with accurate anatomical features.
- Evaluate Model Quality: Assess the model’s accuracy, level of detail, and overall visual appeal. Look for models based on reliable anatomical references and validated data.
- Check File Formats and Software Compatibility: Ensure the chosen model is compatible with your preferred software and operating system. Popular formats include OBJ, STL, and FBX.
- Explore Available Resources: Explore online repositories, educational platforms, and research institutions that offer free 3D models. Some platforms may require registration or membership.
- Utilize Available Tools: Many 3D modeling software programs offer tools for customizing and manipulating models, allowing users to add labels, annotations, and interactive elements.
FAQs about 3D Skin Models
Q: What are the benefits of using 3D skin models over traditional 2D images or diagrams?
A: 3D models offer a more immersive and interactive experience, allowing users to explore the skin’s structure from multiple perspectives. They provide a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and anatomical complexities compared to static 2D representations.
Q: Are there any limitations to using 3D skin models?
A: While 3D models offer significant advantages, they are not without limitations. They are static representations and cannot fully capture the dynamic nature of living tissue. Additionally, the accuracy and detail of the model depend on the data used for its creation.
Q: How can I contribute to the development of 3D skin models?
A: If you have relevant expertise in anatomy, 3D modeling, or software development, you can contribute by creating or refining existing models. You can also share your knowledge and skills with others through online communities and forums.
Conclusion
3D models of human skin are invaluable tools for education, research, and clinical practice. They offer a powerful way to visualize and understand the intricate structure and functions of this vital organ. By leveraging free resources and exploring the vast potential of this technology, we can enhance our understanding of skin health and develop innovative solutions for treating skin diseases. The future of skin research and education is undoubtedly intertwined with the continued development and application of these powerful 3D models.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Guide to 3D Models and Their Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!