Unveiling the Science of Skin Discoloration and Effective Solutions
Related Articles: Unveiling the Science of Skin Discoloration and Effective Solutions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Science of Skin Discoloration and Effective Solutions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Science of Skin Discoloration and Effective Solutions

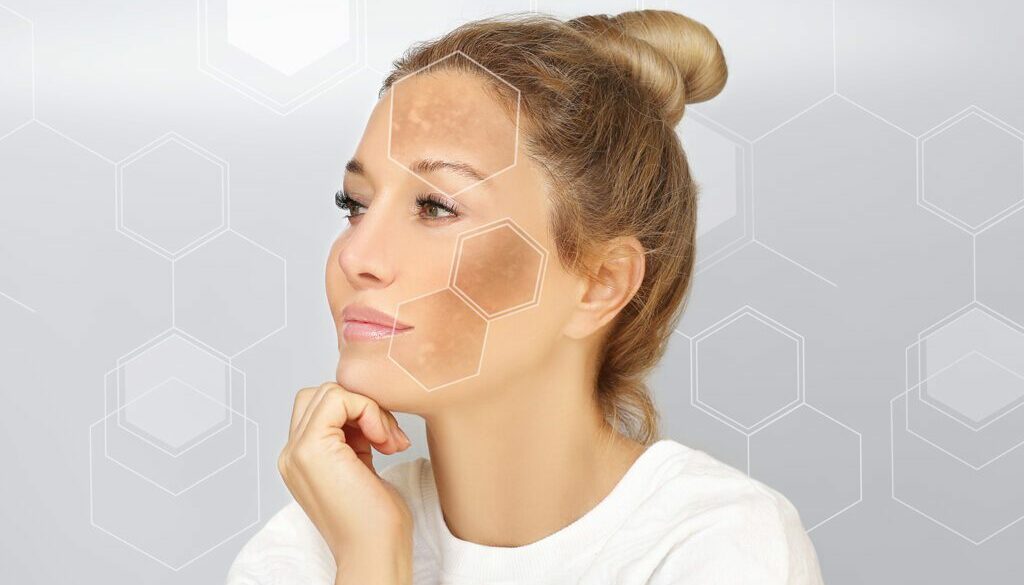
Hyperpigmentation, commonly known as dark spots, is a prevalent skin concern affecting individuals of all skin tones. These blemishes are characterized by areas of increased melanin production, resulting in darker patches on the skin’s surface. While harmless, they can be a source of aesthetic distress, prompting many to seek effective solutions. Understanding the underlying causes and the science behind hyperpigmentation is crucial in selecting the most appropriate treatment options.
The Science Behind Dark Spots:
Melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, is responsible for the natural color of our skin. When the skin is exposed to external stimuli like ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, trauma, inflammation, or hormonal fluctuations, melanocytes are triggered to produce more melanin. This surge in melanin production leads to the formation of dark spots, which can range in size, shape, and intensity.
Types of Hyperpigmentation:
- Melasma: Characterized by brown or gray patches, often appearing on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. It is frequently associated with hormonal changes, pregnancy, and exposure to sunlight.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Occurs after skin injuries like acne, burns, or cuts. The body’s natural healing process involves increased melanin production, resulting in dark marks at the site of injury.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): Develop due to prolonged sun exposure, appearing as flat, brown spots on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and arms.
- Freckles (Ephelides): Small, flat, brown spots, often clustered together, that are genetically predisposed and become more prominent with sun exposure.
Effective Solutions for Hyperpigmentation:
Addressing hyperpigmentation requires a multi-pronged approach that combines topical treatments, professional interventions, and lifestyle modifications.
1. Topical Treatments:
- Hydroquinone: A potent skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. It is available in varying strengths and formulations, often requiring a doctor’s prescription.
- Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote skin cell turnover, reducing hyperpigmentation by exfoliating the skin’s surface and diminishing melanin production.
- Kojic Acid: A natural derivative of fungi that inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin synthesis. It is considered milder than hydroquinone but may require consistent use for noticeable results.
- Azelaic Acid: An effective treatment for mild to moderate hyperpigmentation, especially PIH. It inhibits tyrosinase activity and possesses anti-inflammatory properties.
- Tranexamic Acid: A potent inhibitor of melanin production, often used in combination with other ingredients to enhance its efficacy.
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): A versatile ingredient that reduces melanin production, improves skin barrier function, and minimizes inflammation.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Chemical exfoliants like glycolic acid and lactic acid, which remove the outer layer of skin, promoting cell turnover and reducing hyperpigmentation.
- Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): Exfoliating agents like salicylic acid, which penetrate deeper into the pores, effectively addressing hyperpigmentation caused by acne.
- Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid): A powerful antioxidant that inhibits melanin production, protects against sun damage, and brightens the skin.
2. Professional Treatments:
- Chemical Peels: Chemical solutions applied to the skin to remove the outer layer, promoting cell regeneration and reducing hyperpigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Targeted laser beams remove the top layer of skin, stimulating collagen production and reducing hyperpigmentation.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): A non-invasive treatment that uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Sun Protection: Consistent use of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days, is crucial in preventing further hyperpigmentation and protecting against sun damage.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake promotes skin health and helps maintain its natural barrier function, reducing the likelihood of hyperpigmentation.
- Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can support overall skin health and reduce inflammation.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to hyperpigmentation. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like exercise, yoga, or meditation can promote skin health.
FAQs about Hyperpigmentation and Treatment Options:
Q: How long does it take to see results from hyperpigmentation treatments?
A: The time it takes to see results varies depending on the severity of the hyperpigmentation, the chosen treatment, and individual skin characteristics. Some treatments may show visible improvements within a few weeks, while others may require several months of consistent use.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with hyperpigmentation treatments?
A: Some topical treatments, particularly those containing hydroquinone or retinoids, may cause side effects like dryness, redness, or irritation. Professional treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy can also cause temporary redness, swelling, or peeling. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment and to discuss potential side effects.
Q: What are the best ways to prevent hyperpigmentation?
A: Preventing hyperpigmentation involves protecting the skin from sun damage, avoiding skin trauma, and managing underlying hormonal imbalances. Consistent sunscreen use, gentle skincare routines, and addressing skin concerns promptly are essential preventive measures.
Tips for Effective Hyperpigmentation Treatment:
- Consult a dermatologist: Before embarking on any treatment, it is essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the underlying cause of your hyperpigmentation and receive personalized treatment recommendations.
- Be patient and consistent: Hyperpigmentation treatment requires time and consistency. It is crucial to follow your dermatologist’s instructions carefully and use the prescribed products regularly for optimal results.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Sun exposure can worsen hyperpigmentation. Always apply sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days, and wear protective clothing when exposed to the sun for prolonged periods.
- Avoid harsh scrubs and irritants: Excessive scrubbing or using harsh skincare products can irritate the skin and worsen hyperpigmentation. Opt for gentle cleansers and exfoliants suitable for your skin type.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, adequate hydration, and stress management can support overall skin health and contribute to a brighter complexion.
Conclusion:
Hyperpigmentation, while a common skin concern, is treatable with various effective solutions. Understanding the underlying causes, choosing the right treatment options, and maintaining a consistent skincare routine are key to achieving a more even skin tone. By combining topical treatments, professional interventions, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively address hyperpigmentation and regain a brighter, more radiant complexion. However, it is crucial to remember that every individual’s skin is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Consulting a dermatologist is essential for personalized treatment recommendations and ensuring the best possible outcome.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Science of Skin Discoloration and Effective Solutions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!